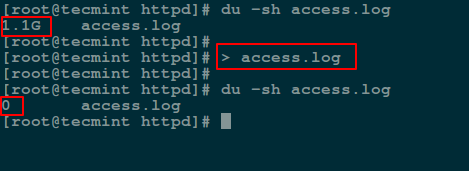
Whether you’re an experienced developer or a beginner trying to establish a secure connection between your computer and a remote Linux server, PuTTY is a tool you can rely on. Let’s delve into understanding how to utilize PuTTY to Secure Shell (SSH) into a Linux machine from a Windows operating system.
Introduction to PuTTY
PuTTY is an open-source, free SSH client for Windows. It enables users to remotely access computers over networks and run commands as if they were sitting in front of the terminal. It’s a versatile tool that’s widely used in network administration, software development, and other IT-related professions.
Downloading and Installing PuTTY
Getting started with PuTTY is straightforward. Head over to the official PuTTY download page and select the appropriate version for your Windows OS. It’s typically best to choose the latest stable version. After downloading the installer, run it, and follow the prompts to successfully install PuTTY on your machine.
Configuring PuTTY for SSH Connections
Before initiating an SSH connection, you need to gather some vital information: the IP address or hostname of the Linux server you’re connecting to, the port number, and your username.
Open PuTTY and you’ll see a configuration window. Under “Session,” in the “Host Name (or IP address)” field, type the IP address or hostname of your Linux server. Ensure the “Port” field is set to 22, which is the default SSH port.
Select SSH under “Connection type” and then move on to the “Saved Sessions” field. Input a name for this connection configuration for future use. Once done, click “Save” to keep these settings. This way, you won’t need to input these details every time you want to establish a connection.
Initiating the SSH Connection
With your session saved, you’re ready to connect. Select your saved session and click “Open.” A new window with a console interface will open, and a prompt will ask for your username. Input the username for your Linux server. Hit “Enter,” and you’ll be asked for your password. Type in your password and hit “Enter” again. Remember, the cursor won’t move while you’re typing your password; this is a standard security feature.
Dealing with PuTTY Security Alerts
The first time you establish a connection, PuTTY will display a security alert to confirm the server’s authenticity. This alert safeguards against potential man-in-the-middle attacks. PuTTY will show the server’s SSH key fingerprint, which you should compare with the fingerprint of your Linux server. If the fingerprints match, click “Yes” to add the server’s host key to PuTTY’s cache. If the alert pops up in subsequent sessions, there’s a possibility your server’s security may have been compromised.


![Install and Use Ventoy on Linux [Step-by-Step Guide]](https://webomate.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/install-and-use-ventoy-on-linux-step-by-step-guide-768x372.png)