FOSS Weekly #23.36: De-Googled Fairphone 5, GNOME 45 Features, Pacman Commands and More
Several distributions released their new versions this week. GNOME 45 is nearing its release with devastating news for the extensions.

Several distributions released their new versions this week. GNOME 45 is nearing its release with devastating news for the extensions.


In the vast realm of networked computers, each device needs a unique identifier—a name that allows it to be distinguishable from the crowd. This unique identifier is known as the “hostname.” Whether you are working in a large corporate network or simply tinkering with a personal Linux box, you might find yourself needing to change this hostname at some point. This comprehensive guide walks you through the process of changing the hostname in Debian 12 BookWorm, one of the latest iterations of the popular Linux distribution Debian.
Before diving into the nitty-gritty, ensure you have the following:
sudo Privileges: Administrative access is necessary to make system-wide changes.To make sure we’re on the same page, let’s clarify some terminology:
sudo: Command that allows permitted users to execute a command as a superuser./etc/hostname and /etc/hosts: Configuration files storing hostname information.It’s always prudent to backup important configurations before making any changes. Open the terminal and run:
cp /etc/hostname /etc/hostname.bak cp /etc/hosts /etc/hosts.bak
This creates backup copies of your current hostname and hosts files.
hostnamectl CommandStep 1: Check Current Hostname
To see your current hostname, run the following command:
hostnamectl
Step 2: Change the Hostname
To change your hostname, execute:
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname new-hostname
Replace new-hostname with your desired hostname. For instance, to change the hostname to “mydebian,” you’d run:
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname mydebian
Step 3: Verify the Changes
Use the hostnamectl command again to check if the hostname has been updated:
hostnamectl
Enjoy live USB with persistence so that your changes made in live sessions are saved. Learn to create a persistent USB in this tutorial.
The post 10 Tools to Take or Capture Desktop Screenshots in Linux first appeared on Tecmint: Linux Howtos, Tutorials & Guides .
Most of the time we need to take screenshots of the whole screen or some part of the window on the screen. While on Android
The post 10 Tools to Take or Capture Desktop Screenshots in Linux first appeared on Tecmint: Linux Howtos, Tutorials & Guides.
![9 Must-Have Linux Console [Terminal] File Managers](https://webomate.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/9-must-have-linux-console-terminal-file-managers.png)
The post 9 Best Linux Console File Managers first appeared on Tecmint: Linux Howtos, Tutorials & Guides .
Linux console file managers can be very helpful in day-to-day tasks, when managing files on a local machine, or when connected to a remote one.
The post 9 Best Linux Console File Managers first appeared on Tecmint: Linux Howtos, Tutorials & Guides.
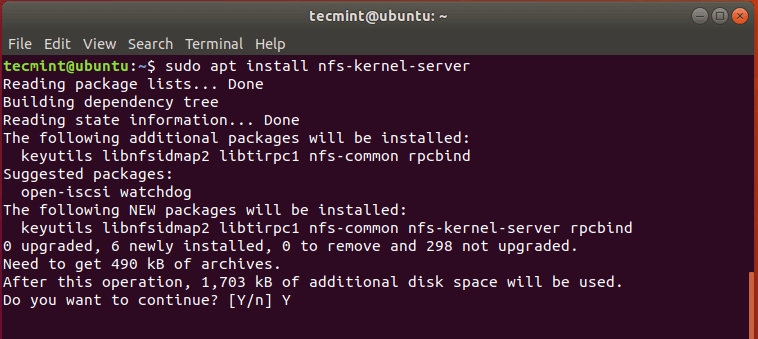
The post How to Install NFS Server and Client on Ubuntu 22.04 first appeared on Tecmint: Linux Howtos, Tutorials & Guides .
NFS (Network File Share) is a protocol that allows you to share directories and files with other Linux clients in a network. The directory to
The post How to Install NFS Server and Client on Ubuntu 22.04 first appeared on Tecmint: Linux Howtos, Tutorials & Guides.
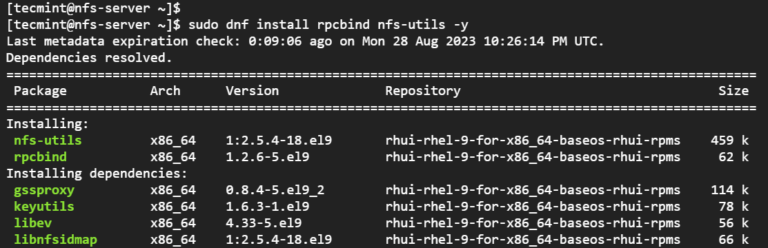
The post How to Install NFS Server and Client on RHEL-based Distributions first appeared on Tecmint: Linux Howtos, Tutorials & Guides .
In Linux, there are a couple of file-sharing protocols used to share storage and files across a network. The most widely used ones are Samba
The post How to Install NFS Server and Client on RHEL-based Distributions first appeared on Tecmint: Linux Howtos, Tutorials & Guides.
You can use a live Linux USB with virtual machines in VirtualBox. It saves you the annoyance of rebooting your host machine.
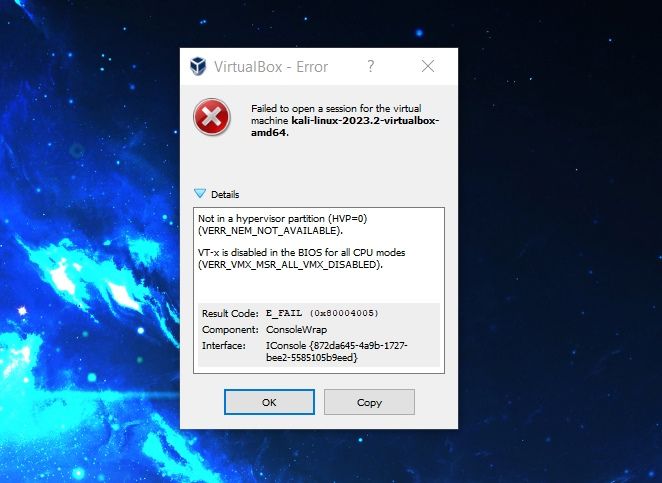
Here are the things you need to make sure that your Windows system is ready to run virtual machines.
The post 5 Most Frequently Used Open Source Shells for Linux first appeared on Tecmint: Linux Howtos, Tutorials & Guides .
The shell is the command interpretor in an operating system such as Unix or GNU/Linux, it is a program that executes other programs. It provides
The post 5 Most Frequently Used Open Source Shells for Linux first appeared on Tecmint: Linux Howtos, Tutorials & Guides.
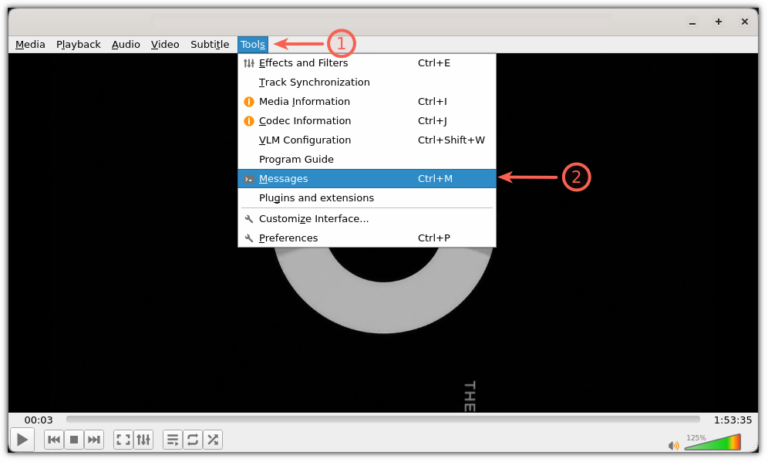
Troubleshooting a video playback issue in VLC? Here’s how you can check the VLC log files.
The post My Favorite Command Line Editors for Linux – What’s Your Editor? first appeared on Tecmint: Linux Howtos, Tutorials & Guides .
Knowing how to edit files quickly and effectively via the command line is vital for every Linux system administrator. File edits are performed on a
The post My Favorite Command Line Editors for Linux – What’s Your Editor? first appeared on Tecmint: Linux Howtos, Tutorials & Guides.


In the expansive universe of Linux distributions, the choice of which one to use can be overwhelming. Among the galaxies of options, two Arch-based stars have shone increasingly brightly: Manjaro and EndeavourOS. Both are rooted in the Arch Linux ecosystem, yet they cater to different kinds of users and offer unique experiences. If you’re currently a Manjaro user contemplating the switch to EndeavourOS, this article aims to help you make an informed decision.
What is Manjaro?
Manjaro is an Arch-based Linux distribution that is designed to be user-friendly and accessible. Known for its ‘Install and Go’ philosophy, Manjaro offers ease of use, making it suitable for Linux newcomers. It comes with a variety of desktop environments like XFCE, KDE, and GNOME, among others. Manjaro also features its own package manager, Pamac, which makes software installation a breeze. Automatic updates and built-in stability checks make it a go-to choice for those who want the power of Arch Linux without its complexities.
What is EndeavourOS?
EndeavourOS is also an Arch-based Linux distribution, but it aims to be closer to vanilla Arch. Targeted at intermediate to advanced users, EndeavourOS offers an almost bare-bones experience with the choice to customize your system as you see fit. While it does come with an installer, it is more manual compared to Manjaro’s Calamares installer. It aims to provide the user with an Arch experience with minimal added features, relying mostly on the Arch User Repository (AUR) and Pacman for package management.
To make an apples-to-apples comparison between Manjaro and EndeavourOS, we’ll evaluate them based on the following criteria:
Ease of Installation
Manjaro offers an incredibly user-friendly installation process via its Calamares installer. It is mostly automated and requires only minimal user interaction.
EndeavourOS, on the other hand, offers a more hands-on installation process. Though it also offers an installer, it allows for more customization during the setup, which might be more appealing to advanced users but intimidating for beginners.
Package Management
Manjaro uses Pamac for package management, which offers a clean, easy-to-use graphical interface. It also supports AUR, enabling a wide range of software availability.
The post 16 Free and Open Source Video Players for Linux in 2023 first appeared on Tecmint: Linux Howtos, Tutorials & Guides .
Audio and Video are two common sources of information sharing we see in today’s world. May it be publishing any product, the need to share
The post 16 Free and Open Source Video Players for Linux in 2023 first appeared on Tecmint: Linux Howtos, Tutorials & Guides.

Kernel 6.5, Kali Linux, Mageia, Firefox, Vivaldi. Plenty of new releases this week.
The post 12 Best Media Server Software for Linux in 2023 first appeared on Tecmint: Linux Howtos, Tutorials & Guides .
A media server is simply a specialized file server or computer system for storing media (digital videos/movies, audio/music, and images) that can be accessed over
The post 12 Best Media Server Software for Linux in 2023 first appeared on Tecmint: Linux Howtos, Tutorials & Guides.
The open source LanguageTool can also be integrated with LibreOffice Writer to provide a better grammatically accurate writing experience.
The post How to Install Universal Media Server to Stream Media to Any Devices first appeared on Tecmint: Linux Howtos, Tutorials & Guides .
Universal Media Server (UMS) is a cross-platform and free DLNA-compliant, HTTP(s) PnP Media server, which provides a number of capabilities such as sharing multimedia files
The post How to Install Universal Media Server to Stream Media to Any Devices first appeared on Tecmint: Linux Howtos, Tutorials & Guides.