How To Install R Programming Language in Linux
R is a popular programming language and software environment used to build statistical and graphical computing tools for data science. It is in many ways similar to the S programming language and environment; R is a different implementation of S. Although there are some significant differences between the two.
R is free software available under the terms of the Free Software Foundation’s GNU General Public License. It is also cross-platform, it can be compiled and run on Linux, and other UNIX-based operating systems including FreeBSD and MacOS; and Windows as well.
R supports a variety of statistical (linear and nonlinear modeling, classical statistical tests, time-series analysis, classification, clustering, etc) and graphical techniques.
R Programming Language’s Key Features
- Offers effective data handling and storage facility.
- Provides a suite of operators for calculations on arrays, in particular matrices.
- Ships with a large, coherent, integrated collection of intermediate tools for data analysis.
- Offers graphical facilities for data analysis and display either on-screen or on hardcopy.
- Provides conditionals, loops, user-defined recursive functions, and input and output facilities.
- Allows users to add additional functionality by defining new functions.
- It’s highly extensible via packages, about eight packages are supplied with the R distribution and many others are available through the CRAN (Comprehensive R Archive Network) family of Internet sites.
- Supports for easily creating well-designed publication-quality plots such as mathematical symbols and formulae where needed, and.
- Most S programs can run unaltered in R.
- Also, for computationally-intensive tasks, C, C++, and Fortran code can be linked and called at run time.
- Ships with comprehensive documentation, in LaTeX-like documentation format.
Installing R Programming Language in Linux
You can install R programming language packages on your Linux system as shown below. On RHEL-based distributions, you need to it from the EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) repository.
Note: Remember to run the correct set of commands for your Linux distribution.
Install R on Ubuntu
$ sudo apt update -qq $ sudo apt install --no-install-recommends software-properties-common dirmngr $ wget -qO- https://cloud.r-project.org/bin/linux/ubuntu/marutter_pubkey.asc | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/cran_ubuntu_key.asc $ sudo add-apt-repository "deb https://cloud.r-project.org/bin/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs)-cran40/" $ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install --no-install-recommends r-base
Install R on Debian
$ sudo apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-key '95C0FAF38DB3CCAD0C080A7BDC78B2DDEABC47B7' $ sudo add-apt-repository "deb https://cloud.r-project.org/bin/linux/debian $(lsb_release -cs)-cran40/" $ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install --no-install-recommends r-base
Install R on Fedora
$ sudo dnf install R
Install R on RHEL Systems
--------- On RHEL 9 ---------
$ sudo subscription-manager repos --enable codeready-builder-for-rhel-9-$(arch)-rpms
$ sudo dnf install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-9.noarch.rpm
$ sudo dnf install R
--------- On RHEL 8 ---------
$ sudo subscription-manager repos --enable codeready-builder-for-rhel-8-$(arch)-rpms
$ sudo dnf install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm
$ sudo dnf install R
--------- On RHEL 7 ---------
$sudo subscription-manager repos --enable rhel-*-optional-rpms
--enable rhel-*-extras-rpms
--enable rhel-ha-for-rhel-*-server-rpms
$ sudo yum install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
$ sudo dnf install R
Install R on CentOS Stream
--------- On CentOS Stream 9 --------- $ sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled crb $ sudo dnf install epel-release epel-next-release $ sudo dnf install R --------- On CentOS Stream 8 --------- $ sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled powertools $ sudo dnf install epel-release epel-next-release $ sudo dnf install R --------- On CentOS 7 --------- $ sudo yum install epel-release $ sudo dnf install R
Install R on Rocky and AlmaLinux
--------- On Rocky and AlmaLinux 9 --------- $ sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled crb $ sudo dnf install epel-release $ sudo dnf install R --------- On Rocky and AlmaLinux 8 --------- $ sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled powertools $ sudo dnf install epel-release $ sudo dnf install R
Install R on openSUSE
$ sudo VERSION=$(grep "^PRETTY_NAME" /etc/os-release | tr " " "_" | sed -e 's/PRETTY_NAME=//' | sed -e 's/"//g') $ sudo zypper addrepo -f http://download.opensuse.org/repositories/devel:/languages:/R:/patched/$VERSION/ R-base $ sudo zypper install R-base R-base-devel
Verify R Installation in Linux
After installing the R packages, you can verify if the environment is set up well. To start the R program, run the R command which will launch the R program shell as shown in the next screenshot.
$ R
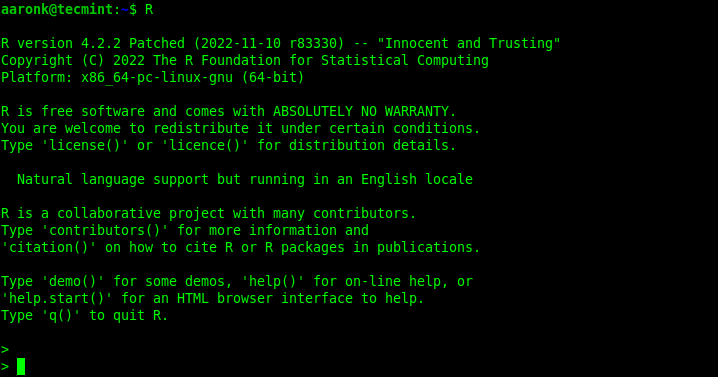
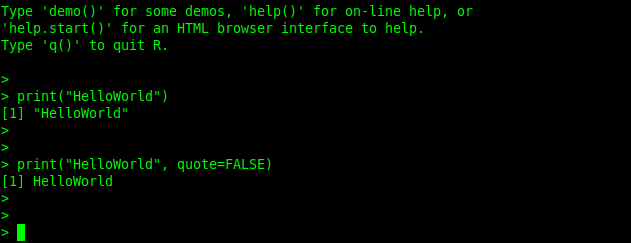
You can run a hello world program in R as shown:
>print("HelloWorld")
>print("HelloWorld", quote=FALSE)
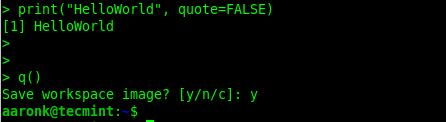
To quit the R program shell, issue the q() command. You will be prompted whether you want to save the data from your R session, enter y for yes or n for no, or c to cancel:
> q()
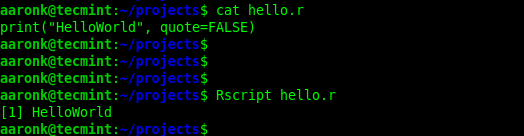
Besides, you can run an R script using the Rscript (front end for scripting with R) command as follows:
$ cat hello.r $ Rscript hello.r
For more usage options, read the R and Rscript man pages:
$ man R $ man Rscript
We have come to the end of this guide. For more information, visit the R project’s official website.