Introduction
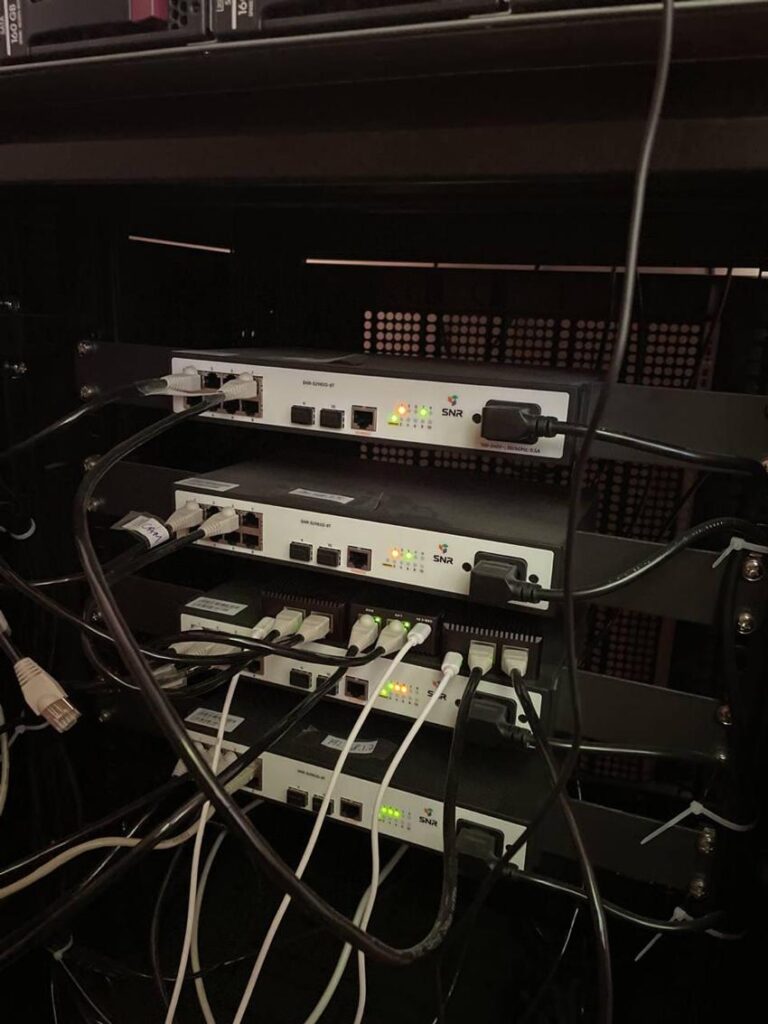
In our previous article we have demonstrated a working prototype of Host Identity Based Virtual Private Service or HIP-VPLS. Back then we used the Mininet framework. Here we are going to demonstrate how to deploy this system on a real hardware. We are going to use NanoPi R2S as the platform for HIP-VPLS. Just a reminder. Virtual Private LAN Services (VPLS) provide means for building Layer 2 communication on top of an existing IP network. VPLS can be built using various approaches. However, when building a production-grade VPLS solution one needs to have a clear picture of how such aspects as security, mobility, and L2 issues will be solved.
Host Identity Protocol (HIP) was originally designed to split the dual role of the IP addresses. In other words, HIP is a Layer 3.5 solution that sits between the IP and transport layers. HIP uses hashes of public keys as identifiers. These identifiers, or Host Identity Tags (HITs), are exposed to the transport layer and never change (well, strictly speaking, they might change if the system administrator will decide to rotate the RSA or ECDSA key pairs for instance, but that will happen rarely). On the other hand, HIP uses routable IP addresses (these can be both IPv4 or IPv6) as locators and are used to deliver the HIP and IPSec packets between the end-points. Overall, to identify each other and exchange secret keys, HIP relies on a 4-way handshake (also known as HIP base exchange, or HIP BEX for short). During the BEX, peers negotiate a set of cryptographic algorithms to be used, identify each other (since HITs are permanent and are bound to public keys HIP can employ a simple firewall based on HITs to filter out untrusted connections), exchange the keys (HIP can use Diffie-Hellman and Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman algorithms), and even protect from Denial of Service attacks using computational puzzles (these are based on cryptographic hash functions and ability of peers to find collisions in hash functions; the complexity of a solution is regulated by a responder in HIP BEX). HIP also supports mobility and uses a separate handshake procedure during which the peer notifies its counterpart about the changes in the locator (read the IP address used for routing purposes).