Ubuntu 22.04: Speed Up Package Updates with Apt-Cacher-NG
Apt-Cacher-NG is a caching proxy server (or apt proxy) for Debian-based distributions such as Ubuntu, Kubuntu, Xubuntu, Edubuntu, Linux Mint, etc. It is used to cache the downloaded packages locally on your server.
Let’s say you have a small network with a few computers attached to it, and you want to install and update software packages on each system manually. Then, it would be a difficult and time-consuming task.
That’s why configuring an apt-cacher-ng on any system would be a great idea, as it caches all the downloaded packages from the internet on the apt-cache server, and the rest of the Debian and Ubuntu machines get them from an apt-cache server, which will save our precious time and internet bandwidth as well.
Here, I’m going to set up a cache server on Ubuntu 22.04. In our office, we use over 30 Ubuntu Desktop clients, 28 Ubuntu-Server VMs including versions 22.04 and 20.04, and 4 Linux Mint Desktops.
However, we use a single cache server running Ubuntu 22.04 LTS Server Edition, and so far, there haven’t been any conflicts with the packages. Now, let’s begin setting up the apt-cache server.
My Server Setup
Apt Cache Server OS : Ubuntu 22.04 LTS Server Apt Cache IP Address : 192.168.0.125 Apt Cache Hostname : aptcacher.tecmint.lan Default Port : 3142
My Client Setup
Client OS : Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Client IP Address : 192.168.0.3 Client Hostname : client.tecmint.lan
Step 1: Installing Apt-Cacher-NG on the Ubuntu Server
First, log into the server to open a terminal using the’Ctr+Alt+T‘ and install apt-cacher-ng package using the following apt command.
sudo apt-get install apt-cacher-ng
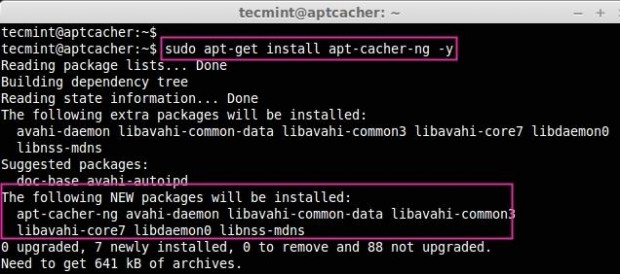
After installation is completed, the apt-cacher-ng will start automatically. Now open and edit the cache-ng configuration file located under the ‘/etc/apt-cacher-ng‘ directory.
sudo vim /etc/apt-cacher-ng/acng.conf
Next, we need to uncomment the following lines as suggested, if it is commented remove the ‘#‘ from the beginning. In this directory, all dpkg packages will be stored while installing or updating packages.
CacheDir: /var/cache/apt-cacher-ng
To enable the log we need to enable this line, By Default it will be enabled.
LogDir: /var/log/apt-cacher-ng
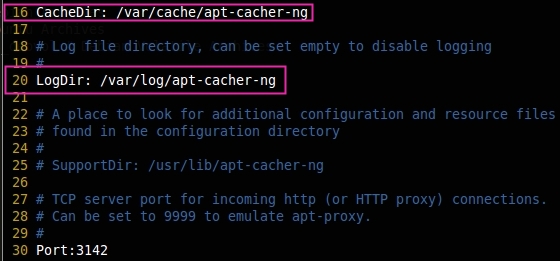
The apt-cacher will listen to port 3142, if you need to change the port, you can change the port.
Port:3142
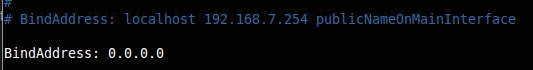
Next, add the line ‘BindAddress: 0.0.0.0‘ entry below the line says:
# BindAddress: localhost 192.168.7.254 publicNameOnMainInterface BindAddress: 0.0.0.0
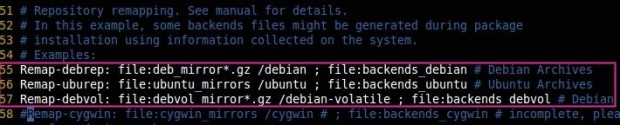
Here we can define the distributions such as Ubuntu and Debian, which all need to be cached.
Remap-debrep: file:deb_mirror*.gz /debian ; file:backends_debian # Debian Archives Remap-uburep: file:ubuntu_mirrors /ubuntu ; file:backends_ubuntu # Ubuntu Archives Remap-debvol: file:debvol_mirror*.gz /debian-volatile ; file:backends_debvol # Debian Volatile Archives
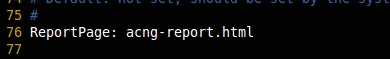
If we need to get the reports of apt-cache in the web interface, we need to enable the following line, but by default, this will be enabled.
ReportPage: acng-report.html
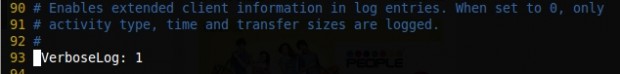
To get more information about ‘log‘, we have to uncomment the below line, If we set it to 0 Only the activity type, time, and size of our package transfer will be logged.
VerboseLog: 1
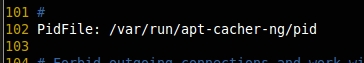
To run the apt-cacher service, we need to enable the pid file in the configuration.
PidFile: /var/run/apt-cacher-ng/pid
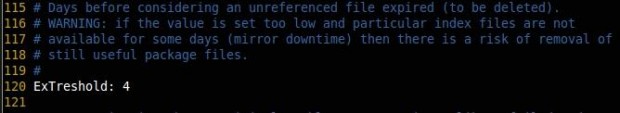
To remove the unreferenced files.
ExTreshold: 4
Finally, we’ve done with the configuration, save and close the file. Now we are all set to restart the apt-cacher-ng service using the following command.
$ sudo /etc/init.d/apt-cacher-ng restart
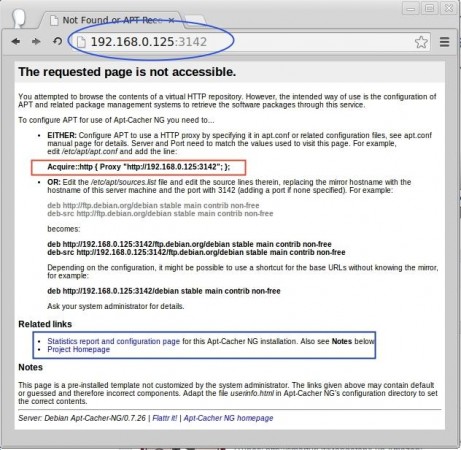
Access the report page of apt-cacher-ng in the web interface using the below URL.
http://192.168.0.125:3142/
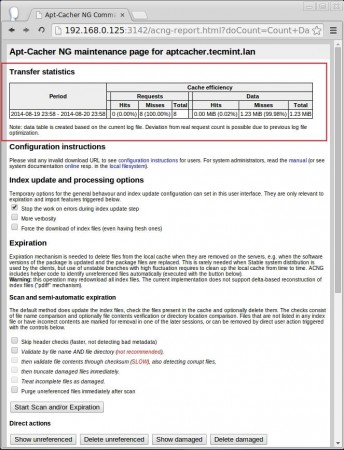
Here we can see the report page for apt-cacher-ng, click the static report and configuration page at the bottom of this page to get the Download hits and misses.
From the report home page we need to copy the Proxy URL for later use. We can even install packages in this server from apt-cache which can be configured locally, by just adding the below entry in /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/02proxy.
Acquire::http { Proxy "http://192.168.0.125:3142"; };
Step 2: Ubuntu Client Side Configuration
First login into the client machine (Ubuntu/Debian) and create a ‘02proxy‘ file under the ‘/etc/apt/apt.conf.d/‘ directory.
sudo vim /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/02proxy
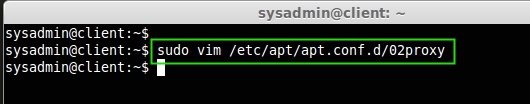
Now copy the Acquire URL and append it to the 02proxy file. You will get the following URL from the apt-cacher-ng access report page at http://192.168.0.125:3142/.
Acquire::http { Proxy "http://192.168.0.125:3142"; };
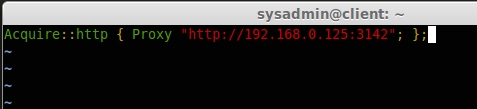
Save and exit using wq!. Hereon, if any packages are downloaded on the client machine will be cached to the apt-cache server.
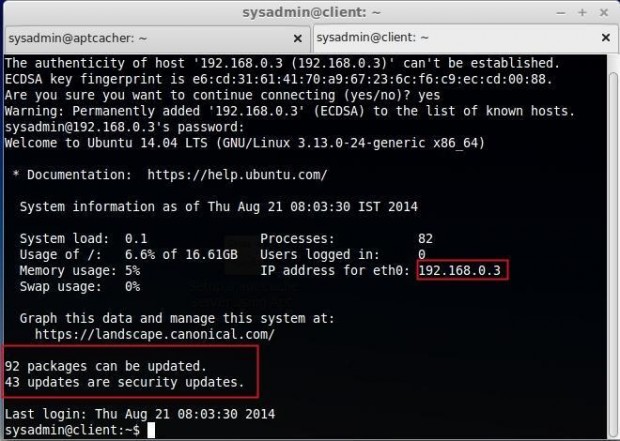
In my client machine, 92 packages can be updated, and 43 updates are available for security updates. We have already applied the same updates for the cache server. So, that the packages will now be cached in apt-cacher. If I’m updating this client machine it won’t take too much time to get packages from the internet.
Now update the repository and upgrade the packages.
$ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get upgrade
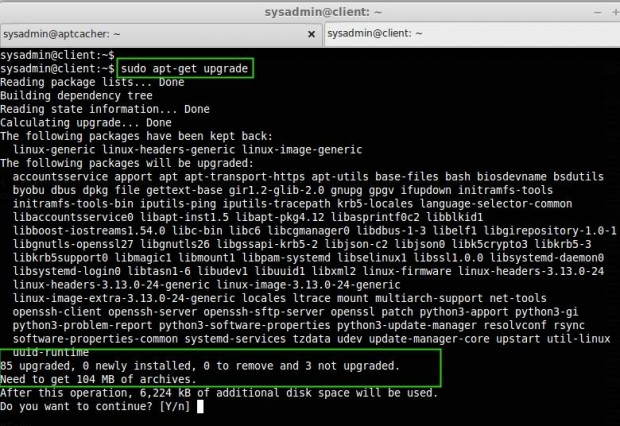
In the above screens, it shows that we need to update 85 packages and its size is 104MB, let us see how long it will take to fetch the package.
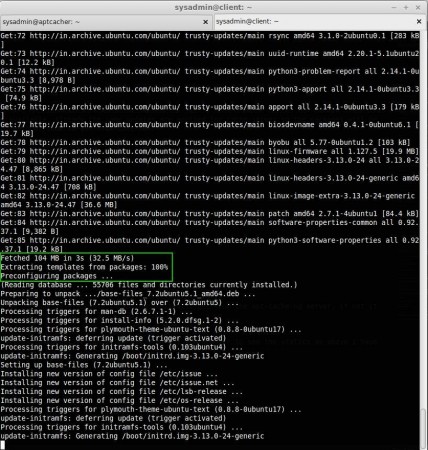
I’m not even in a data center, I’m just using a 256Kbps internet connection where the download speed will just be 50Kbps to 60Kbps. But see the below image of how it fetched 104MB in 3 Seconds. That’s because it is already cached in the apt-cacher-ng server.
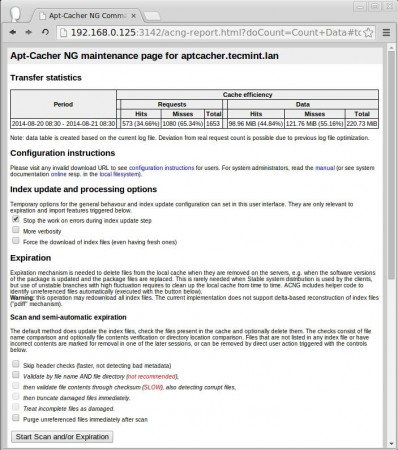
If we need to see Cache Count data, which we have downloaded, we can access ip:port (192.168.0.125:3142) in any web browser to see the statistics, as I have explained above.
While we download any packages to install in any Debian/Ubuntu machines, If the package is available in apt-cache it will get from the apt-cache-ng server, if not it will fetched from the internet to the local repository for future use.
In this article, we have seen how to set up a local cache server for apt packages using apt-cacher-ng, many people want this setup to save their time and bandwidth. I hope this will help all those who use Debian/Ubuntu machines.